Clinical Site
Accumetra CT Image Quality Assurance for Clinical Sites
Medical scanners and image analysis software systems are now routinely being used to obtain precise quantitative image measurements, which can often play a major role in patient care. It is therefore critical that clinical sites verify that their medical scanning equipment, including image acquisition protocols and analysis software, have been thoroughly evaluated to achieve high levels of performance for specific measurement tasks. Fortunately, Accumetra has developed the requirements and technical performance needed for quantitative CT image measurement tasks.
Achieving accurate volume measurements of small (6 to 10 mm diameter) solid lung nodules is critical to determining the malignancy potential of suspicious lung nodules that are identified in the standard care setting as well as in CT lung cancer screening. Although it may appear that current CT scanners are more than capable of reliably performing these quantitative measurements with high quality due to their ability to obtain sub-millimeter resolution lung images, many clinical sites are not taking the steps needed to achieve consistent high quality small lung nodule measurement results. A study of volume measurement performance in a phase II clinical trial observed multiple clinical sites using CT scanners which resulted in errors in volume change measurements as high as 43% [1]. In addition, a 2016 crowd-sourcing study of CT scanner image quality performance using a site’s low dose CT lung cancer screening acquisition protocol revealed that 37% of sites used insufficient slice thickness (<= 1.25mm slice thickness is needed) and only 19% of sites used the needed slice thickness and a reconstruction kernel that avoided excessive smoothing and avoided high levels of edge enhancement [2]. Poor CT image acquisition performance has the potential to result in high variability in lung nodule volume measurement performance, which can negatively impact patient care by contributing to unnecessary biopsies and delays in early lung cancer diagnosis.
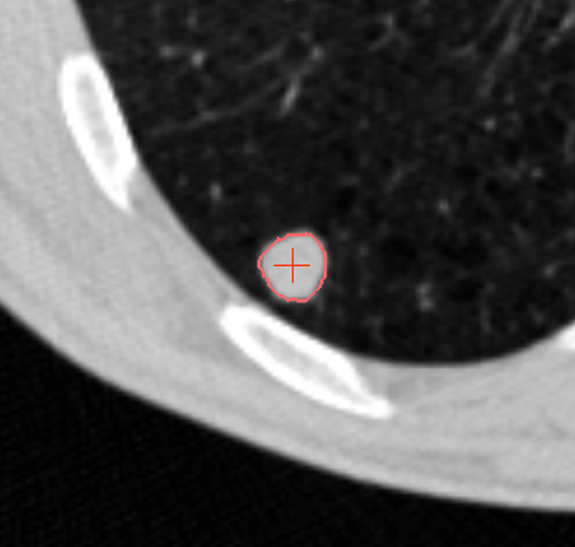
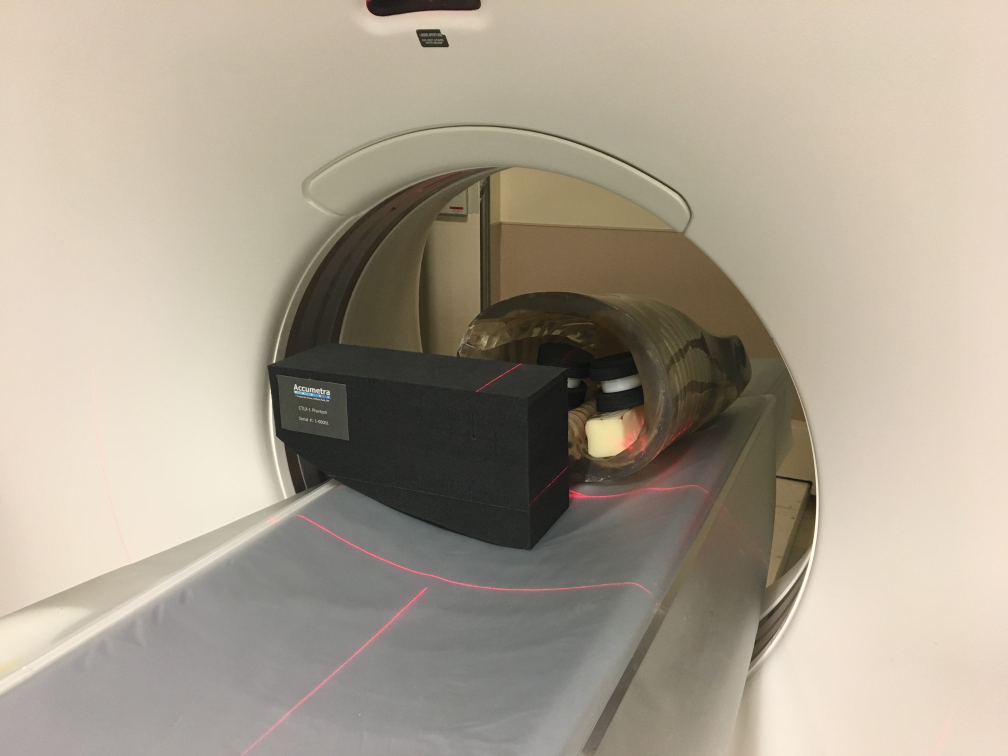
Accumetra’s CT Image Quality Assurance (ACQA) service provides guidance to sites on steps needed to achieve high quality lung nodule measurements and provides easy to use tools and resources to verify that a CT scanner, CT image acquisition protocol, and analysis software have the necessary performance to achieve high quality results. A site is provided with a CTLX1 phantom and is given access to upload phantom scans to Accumetra’s phantom analysis service and receive back automated and easy to read phantom analysis reports. Clinical sites are also expected to test the performance of their nodule volume analysis software on clinical zero change CT datasets and synthetic nodule CT scan datasets.
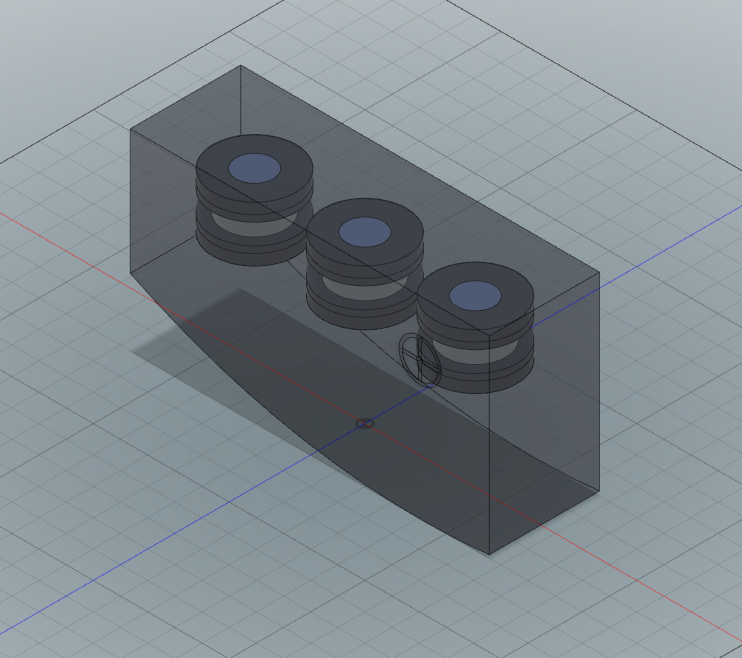
To use this service , a clinical site must register and pay $1,950 + tax for three years of conformance certification services for each CT scanner that is being used for small lung nodule measurements. In addition, the clinical site is recommended to purchase one CTLX1 phantom for each co-located group of CT scanners that will be under an ACQA service contract. The cost of one CTLX1 phantom is $390 + shipping and tax.
For more information, see the QIBA Conformance Certification Service Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ). Register References [1] Henschke CI, Yankelevitz DF, Yip R, Archer A, Zahlmann G, Krishnan K, Helba B, Avila R, “Tumor volume measurement error using computed tomography imaging in a phase II clinical trial in lung cancer.” Journal of Medical Imaging 3(3), 035505 (Jul–Sep 2016). [2] Avila R, Yankelevitz D, Yip R, Henschke C, “P1.03-021 Initial Results from A Novel and Low Cost Method For Measuring CT Image Quality,” January 2017. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 12(1):S554-S555.